Différences entre les versions de « VBTutorial4 »
| Ligne 11 : | Ligne 11 : | ||
| − | + | ||
=BLW method & HuLiS program= | =BLW method & HuLiS program= | ||
| − | + | ||
{| class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" | {| class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Ligne 36 : | Ligne 36 : | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | = BLW within GAMESS (Version: MAR-25-2010 R2) | + | {| class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" |
| + | |- | ||
| + | !<big><big><big>'''BLW within GAMESS (Version: MAR-25-2010 R2)'''</big></big></big> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
[[BLW | BLW ]] is provided by [http://homepages.wmich.edu/~ymo/ Yirong Mo] (Western Michigan University - USA). It allows to optimize local wave function. | [[BLW | BLW ]] is provided by [http://homepages.wmich.edu/~ymo/ Yirong Mo] (Western Michigan University - USA). It allows to optimize local wave function. | ||
Gradients are available for geometry optimization. DFT approaches allow to include a part of correlation into the structure. | Gradients are available for geometry optimization. DFT approaches allow to include a part of correlation into the structure. | ||
| Ligne 49 : | Ligne 52 : | ||
[[BLW | BLW help]] | [[BLW | BLW help]] | ||
| − | = HuLiS : a Huckel-based code | + | |} |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !<big><big><big>'''HuLiS : a Huckel-based code'''</big></big></big> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
[[File:hulis.png|thumb|right| 100px|alt=Huckel - Lewis alt text | Huckel - Lewis]] | [[File:hulis.png|thumb|right| 100px|alt=Huckel - Lewis alt text | Huckel - Lewis]] | ||
| Ligne 62 : | Ligne 72 : | ||
Seminal papers are [http://wiki.lct.jussieu.fr/workshop/images/4/43/HL-CI-JCEp1056.pdf HL-CI] and [http://wiki.lct.jussieu.fr/workshop/images/d/d3/HLP2008.pdf HLP]. | Seminal papers are [http://wiki.lct.jussieu.fr/workshop/images/4/43/HL-CI-JCEp1056.pdf HL-CI] and [http://wiki.lct.jussieu.fr/workshop/images/d/d3/HLP2008.pdf HLP]. | ||
| − | = Paper Exercices | + | |} |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !<big><big><big>'''Paper Exercices'''</big></big></big> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |||
Here are two HuLiS exercices : find the weights in formamide with HL-CI and use HLP to get coefficients for the allyl radical. | Here are two HuLiS exercices : find the weights in formamide with HL-CI and use HLP to get coefficients for the allyl radical. | ||
| Ligne 108 : | Ligne 126 : | ||
This drawback can be shown using the energies of the occupied Huckel orbitals <math> \epsilon_1=\alpha+1.41\beta</math> and<math> \epsilon_2=\alpha</math> | This drawback can be shown using the energies of the occupied Huckel orbitals <math> \epsilon_1=\alpha+1.41\beta</math> and<math> \epsilon_2=\alpha</math> | ||
| − | + | |} | |
| + | |||
| + | {| class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !<big><big><big>'''Computer Exercices'''</big></big></big> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
== Exercice 1 (Lewis structures of benzene, resonance) == | == Exercice 1 (Lewis structures of benzene, resonance) == | ||
| − | = | + | |
| + | {| class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !<big>'''Topic'''</big> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
The benzene molecule is commonly represented as the resonance between the two Kékulé structures. The aim of the exercise is to understand the relative importance of the different Lewis structures in the benzene molecule using BLW and [http://www.hulis.free.fr/ HuLis]. | The benzene molecule is commonly represented as the resonance between the two Kékulé structures. The aim of the exercise is to understand the relative importance of the different Lewis structures in the benzene molecule using BLW and [http://www.hulis.free.fr/ HuLis]. | ||
According to IUPAC’s Goldbook, resonance energy is defined as “The difference in potential energy between the actual molecular entity and the contributing structure of lowest potential energy”. However this definition does not precise what is the geometry of the contributing structure of lowest potential energy. Consequently, we can define two types of resonance energy: the vertical resonance energy (VRE) and the adiabatic resonance energy (ARE). This exercice tutorial will guide us toward Lewis structures and resonance of benzene. | According to IUPAC’s Goldbook, resonance energy is defined as “The difference in potential energy between the actual molecular entity and the contributing structure of lowest potential energy”. However this definition does not precise what is the geometry of the contributing structure of lowest potential energy. Consequently, we can define two types of resonance energy: the vertical resonance energy (VRE) and the adiabatic resonance energy (ARE). This exercice tutorial will guide us toward Lewis structures and resonance of benzene. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | |||
The cc-pVTZ basis set will be used in the following, unless a different choice is specified. | The cc-pVTZ basis set will be used in the following, unless a different choice is specified. | ||
| Ligne 142 : | Ligne 171 : | ||
::Note the value of <math>{\tau}</math>, and the weight of all Lewis structures needed ([Results]). | ::Note the value of <math>{\tau}</math>, and the weight of all Lewis structures needed ([Results]). | ||
| − | |||
[[VBFile 4-1 | all input files are there]] | [[VBFile 4-1 | all input files are there]] | ||
| Ligne 175 : | Ligne 203 : | ||
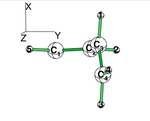
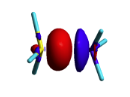
BLW energy decomposition analysis can be used to shed light into the nature of intermolecular interactions. Example of NH3∙∙∙BH3. Visualize the polarization and electron transfer effects using the electron density difference (EDD) maps. | BLW energy decomposition analysis can be used to shed light into the nature of intermolecular interactions. Example of NH3∙∙∙BH3. Visualize the polarization and electron transfer effects using the electron density difference (EDD) maps. | ||
| + | {| class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !<big>'''Geometry'''</big> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
the geometry of the complex we use is | the geometry of the complex we use is | ||
<html><pre> | <html><pre> | ||
| Ligne 190 : | Ligne 223 : | ||
$END | $END | ||
</pre></html> | </pre></html> | ||
| + | |} | ||
*1/ Make orbitals of BH3 alone (then NH3) in the geometry of the complex | *1/ Make orbitals of BH3 alone (then NH3) in the geometry of the complex | ||
| Ligne 197 : | Ligne 231 : | ||
*3/ Let delocalize. This is just a standard DFT calculation. | *3/ Let delocalize. This is just a standard DFT calculation. | ||
| − | '''Preliminary Remarks :''' | + | {| class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" |
| + | |- | ||
| + | !<big>'''Preliminary Remarks :'''</big> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
B3LYP calculation in Gamess is specified in $CONTRL : | B3LYP calculation in Gamess is specified in $CONTRL : | ||
<pre> $CONTRL SCFTYP=RHF DFTTYP=B3LYP runtyp=energy maxit=200 icharg=0 $END</pre> | <pre> $CONTRL SCFTYP=RHF DFTTYP=B3LYP runtyp=energy maxit=200 icharg=0 $END</pre> | ||
| Ligne 203 : | Ligne 241 : | ||
<pre> $BASIS GBASIS=N31 NGAUSS=6 NDFUNC=1 $END</pre> | <pre> $BASIS GBASIS=N31 NGAUSS=6 NDFUNC=1 $END</pre> | ||
| − | '''Step by step help :''' | + | |} |
| + | |||
| + | {| class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !<big>'''Step by step help :'''</big> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
*1/ Perform a NH3 BLW calculation of the fragment alone in the geometry of the complex with '''$BLW NBLOCK=1 $END''' and keep the generated .blw file for next step (same for BH3). | *1/ Perform a NH3 BLW calculation of the fragment alone in the geometry of the complex with '''$BLW NBLOCK=1 $END''' and keep the generated .blw file for next step (same for BH3). | ||
| Ligne 243 : | Ligne 287 : | ||
see also [[VBFile_4-4#gaussiancube.com | gaussiancube file]] | see also [[VBFile_4-4#gaussiancube.com | gaussiancube file]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
[[VBFile 4-4 | all input files are there]] | [[VBFile 4-4 | all input files are there]] | ||
| − | + | |} | |
Version du 28 juin 2012 à 22:34
How to modify this page :
- first : log in (top right of this page) ;
- click on [edit] (far right) to edit a section of the page ;
- write your text directly in the wiki page, and click on the "Save page" button (bottom left) to save your modifications
Pictures : how to insert a picture in your text
See also this page for an introduction to the basics of the wiki syntax
BLW method & HuLiS program
| To the tutors |
|---|
| Sason remarks and prospective 2 hours talk
Philippe's remark on the initially proposed tutorial. are included in bold. Qualitative
Computational Proposal from Yirong
|
| BLW within GAMESS (Version: MAR-25-2010 R2) |
|---|
|
BLW is provided by Yirong Mo (Western Michigan University - USA). It allows to optimize local wave function. Gradients are available for geometry optimization. DFT approaches allow to include a part of correlation into the structure. Structures can interact with $BLWCI group. During the workshop, a BLW computation of file.inp is obtained with the command "blwrun file " file.log and file.blw are in the current directory. |
| HuLiS : a Huckel-based code |
|---|
|
HuLiS is provided by Stephane Humbel (Aix-Marseille Université - France). This is a graphical java applet that deals with Huckel and Lewis structures. It computes coefficients and weights of mesomeric structures through two different approaches: the energy related approach is a simulated CI (HL-CI - deprecated); the wave function approach is a projection of Lewis structures onto a Huckel derived wave function(HLP). This second approach is more reliable. HuLiS is launch with the command "java -jar ~/bin/hulis.jar" or via the web site HuLiS Details of the principles are written at HL-CI and HLP explanations. Seminal papers are HL-CI and HLP. |
| Paper Exercices |
|---|
|
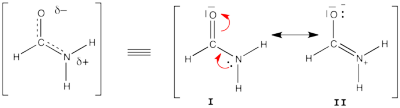
Here are two HuLiS exercices : find the weights in formamide with HL-CI and use HLP to get coefficients for the allyl radical. Formamide with HL-CIFormamide can be written as a resonance between two Lewis strutures. We shall find the weights of this scheme using HL-CI. In HL-CI we define an effective CI hamiltonian that concerns the interaction between the (localized) Lewis structures <math> \Psi_{I}</math> and <math> \Psi_{II}</math>: <math> \Psi_{HL-CI}=c_{I}\Psi_{I}+c_{II}\Psi_{II}</math>. This CI must give the Huckel energy of the delocalized wave function. <math> E_{HL-CI}=E_{Huckel}</math> Formamide's Huckel energy <math>E_{Huckel}= 4\alpha + 6.548\beta</math> The (localized) Lewis structures I and II have an energy of
These values are used as <math>H_{I-I}</math> and <math>H_{II-II}</math> for the CI matrix.
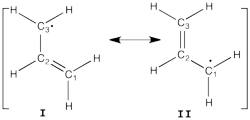
<math> \Psi_{HL-CI}=0.81\Psi_{I}+0.58\Psi_{II}</math>, hence the weights of the structures (I/II)=(66%/34%) Note that in HL-CI <math><Psi_{I}|\Psi_{II}>=0</math> Allyl Radical with HLPAllyl radical can be written as a resonance between two Lewis strutures: <math> \Psi_{HLP}=c_{I}\Psi_{I}+c_{II}\Psi_{II}</math>. We shall find the coefficients of this CI via HLP. The Huckel orbitals are considered as :
In the following the Huckel wave function is expressed as a Salter determinant: <math> \Psi_{Huckel}=|\phi_{1}\bar{\phi_{1}}\phi_2|</math> In the HLP scheme we search the coefficient of the structures I and II by projection of the Huckel wave function onto the localized structures <math> \Psi_{I}=|\pi_{12}\bar{\pi_{12}}p_3|</math> and <math>\Psi_{II}=|p_1\pi_{23}\bar{\pi_{23}}|</math>. Overlap between Lewis structuresWithin Huckel approximation, (<math> <p_{i}|p_{j}>=\delta_{ij}</math>)
Find <math>c_I</math> and <math>c_{II}</math> by solving the equations that derive from
This drawback can be shown using the energies of the occupied Huckel orbitals <math> \epsilon_1=\alpha+1.41\beta</math> and<math> \epsilon_2=\alpha</math> |
| Computer Exercices | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Exercice 1 (Lewis structures of benzene, resonance)
1/ Vertical Resonance Energy - at the geometry of benzene. With the BLW program, and using the provided optimized geometry of benzene molecule, define one 1,3,5-cyclohexadiene Lewis structure, and optimize it's orbitals. 4 blocks need to be defined 3 blocks for 3 pi bond, one for all the sigma electrons.
Exercice 2 (allyl)
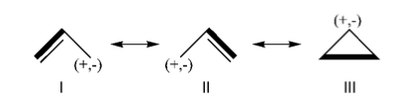
Exercice 3 (Butadiene deconjugation without hyperconjugation)Examine the conjugation in planar butadiene and the hyperconjugation in perpendicular butadiene, and explain the rotational barrier. Note that often people rotate one participating group to disable the conjugation and use the barrier to measure the conjugation energy. What is the inconvenience of this approach? BLW shall be used
Exercice 4 (BH3... NH3) electronics at the B3LYP 6-31G(d) levelBLW energy decomposition analysis can be used to shed light into the nature of intermolecular interactions. Example of NH3∙∙∙BH3. Visualize the polarization and electron transfer effects using the electron density difference (EDD) maps.
|