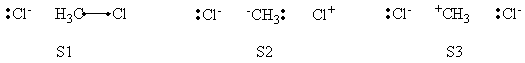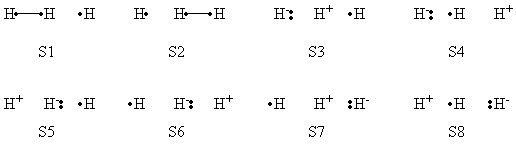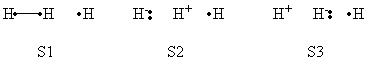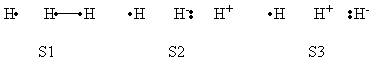Différences entre les versions de « VBTutorial3 »
| (9 versions intermédiaires par 3 utilisateurs non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 1 : | Ligne 1 : | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[VB_tutorial|<<< VB tutorials main page]] |
| Ligne 31 : | Ligne 31 : | ||
## minimal structures for reactant; | ## minimal structures for reactant; | ||
## minimal structures for product. | ## minimal structures for product. | ||
| + | # How would you define your different fragment orbitals for this calculation (''$frag'' section) ? You will find the answer for this case is in the [[General_guidelines_for_BOVB_calculations#Recommended_definition_for_the_orbital_blocks|"recommended definition for the orbital blocks" section of the "practical for BOVB calculations" document]] | ||
# Perform <math>\pi</math>-D-BOVB calculation for reactant [[General_guidelines_for_BOVB_calculations#High_symmetry_case:|(see "high symmetry cases" here)]]: | # Perform <math>\pi</math>-D-BOVB calculation for reactant [[General_guidelines_for_BOVB_calculations#High_symmetry_case:|(see "high symmetry cases" here)]]: | ||
## Perform all-structure <math>\pi</math>-D-BOVB calculation as following: | ## Perform all-structure <math>\pi</math>-D-BOVB calculation as following: | ||
| Ligne 47 : | Ligne 48 : | ||
# Compute the Barrier height of the <math>\textrm{S}_{\textrm{N}}2</math> reaction in both vacuum and solution. See the difference of the barrier heights, and find out the reason. | # Compute the Barrier height of the <math>\textrm{S}_{\textrm{N}}2</math> reaction in both vacuum and solution. See the difference of the barrier heights, and find out the reason. | ||
# Compare the energies of reactant and product structures at reactant and transition state geometries, in both vacuum and solution. What's the difference of the energies at different points? Why? | # Compare the energies of reactant and product structures at reactant and transition state geometries, in both vacuum and solution. What's the difference of the energies at different points? Why? | ||
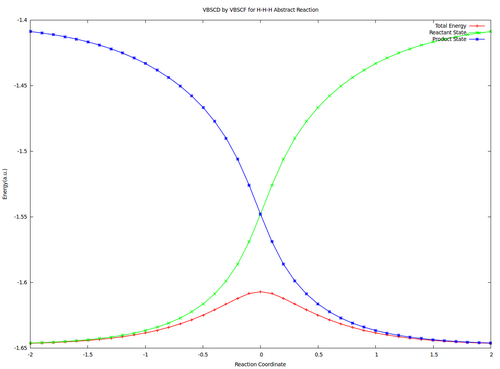
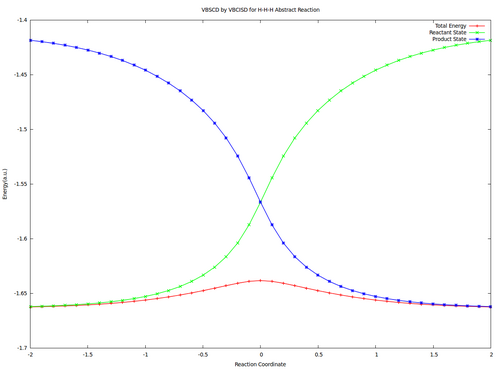
| − | # Compute the resonance | + | # Compute the resonance energy at the crossing point of diabatic curves state points in vacuum. |
{| class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" | {| class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" | ||
| Ligne 143 : | Ligne 144 : | ||
! scope="col" | VBSCF | ! scope="col" | VBSCF | ||
! scope="col" | BOVB | ! scope="col" | BOVB | ||
| − | |||
! scope="col" | BOVB/PCM | ! scope="col" | BOVB/PCM | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row" | All Structures | ! scope="row" | All Structures | ||
| − | | -36.98034 ||-37.02508 | + | | -36.98034 ||-37.02508 || -37.11346 |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row" | Reactant | ! scope="row" | Reactant | ||
| − | | -36. | + | | -36.95984 || -36.98719 || -37.07951 |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row" | Product | ! scope="row" | Product | ||
| − | | -36. | + | | -36.95984 ||-36.98718 || -37.07949 |
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row" | Resonance Energy | ! scope="row" | Resonance Energy | ||
| − | | | + | | 12.9 || 23.8 || 21.3 |
|} | |} | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" | {| class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" | ||
| Ligne 180 : | Ligne 178 : | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |||
=====Weights of Structures===== | =====Weights of Structures===== | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| Ligne 353 : | Ligne 352 : | ||
b - Let us express the various energies and matrix elements in terms of the usual <big><math> \beta </math></big> and <big><math> S </math></big> integrals between the X and H orbitals: | b - Let us express the various energies and matrix elements in terms of the usual <big><math> \beta </math></big> and <big><math> S </math></big> integrals between the X and H orbitals: | ||
| − | <big><math> E_{ind} = | + | <big><math> E_{ind} = \beta S </math></big> |
<big><math> S_{12} = 0.5 </math></big> | <big><math> S_{12} = 0.5 </math></big> | ||
Dernière version du 18 janvier 2013 à 15:56
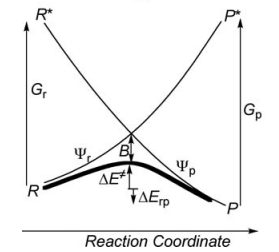
Valence Bond State correlation diagrams
Exercise 1 : Computation of state correlation Diagrams for a 3 centers / 4 electrons system
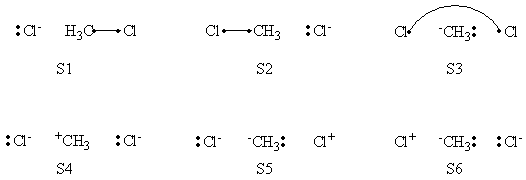
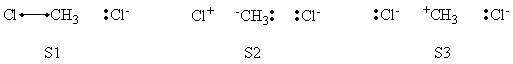
In this exercise the <math>\textrm{S}_{\textrm{N}}2</math> reaction Cl<math>{}^{-}</math> + CH<math>{}_3</math>Cl -> ClCH<math>{}_3</math> + Cl<math>{}^{-}</math> will be studied in both vacuum and solution. Valence Bond State Correlation Diagrams (VBSCD) will be constructed at <math>\pi</math>-D-BOVB level. There are two parts in this exercise: basic part and optional part. The basic part is performed with MCP-DZP basis set in which the inner orbitals in Cl and C are described with MCP pseudo potential. The optional part is performed with 6-31+G* basis set, using the general specification for the xmvb input (expert users). Only reactant and transition state will be computed in this exercise, which is sufficient to build the VBSCD diagrams.
| Note:How to perform a VBPCM calculation |
|---|
|
A VBPCM calculation is performed in the similar way as the VB calculations in vacuum. One should prepare a GAMESS input file with solvent assigned such as: The details of PCM calculation in the GAMESS can be found in GAMESS manual. Keyword "VBTYP=XMVB" in CONTRL section is also essential. After the GAMESS input file is prepared, an XMI file with keyword "VBPCM" should be prepared with the same file name as GAMESS input file. In the current XMVB package, VBSCF/PCM and BOVB/PCM calculations are both supported. |
| Basic part | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1. Compute the Energies and Wavefunctions at Reactant and Transition State with Different Sets of VB StructuresWe advise you to create the first xmvb input file (.xmi file) for this study starting from a .xmi file taken from tutorial1 as a template. Alternatively, you may copy the input file corresponding for the first calculation of this study (L-VBSCF on reactant state geometry in vacuum) from the answer folder of this exercise (cp answer/rs_vac_vbscf.xmi .), run directly the first calculation, inspect input/outputs, and then use this .xmi file as a template for the following calculations.
2. Analysis: Wavefunctions and Energies
|