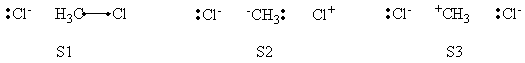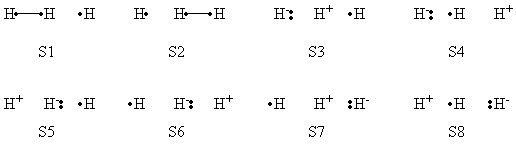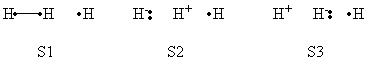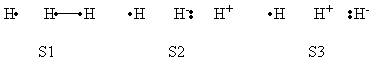Exercise 2 : computation of H—H + H. -> H. + H—H radical exchange VBSCD diagram
1/ Paper exercise :
a/ Considering the following radical exchange process:
<math>
X^{\bullet} + A-Y \rightarrow X-A + ^{\bullet}Y
</math> (X = A = Y = hydrogen atom)
Write the HL wave functions for R and R* and derive the value of G using semiempirical VB theory. Hints : 1) write the wave functions of R and R* so that their overlap is positive; 2) neglect the overlap beween the external atoms X and Y, and neglect the overlap between two different determinants.
b/ Considering the following reaction:
<math>
X^{\bullet} + H-X \rightarrow X-H +^{\bullet}X
</math>
Use semiempirical VB theory to derive the following expression for the avoided crossing term <math> B </math> :
<math>B = 0.25\Delta E_{ST} </math>'
where <math>\Delta E_{ST} </math>' is the singlet-triplet transition energy of the X-H bond at the geometry of the transitions state.
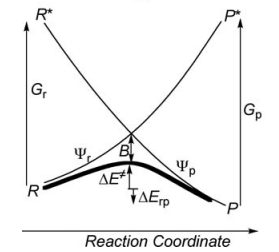
Indication: the resonance energy arising from the mixing of two degenerate VB structures is given by the following expression:
<math>RE = [H_{12}-E_{ind}S_{12}]/(1+S_{12}) </math>
where <math> E_{ind} </math> is the energy of an individual VB structure, and <math> S_{12} </math> and <math> H_{12} </math> are respectively the overlap and Hamiltonian matrix element between R and R*.
c/ It is known that for strong binders, at any given bonding distance the singlet-triplet transition energy is larger than twice the bonding energy of the dimer at equilibrium distance, so that one can write the approximate expression <math>\Delta E_{ST} </math>' <math> = 2 BDE </math>, where <math> BDE </math> is the bonding energy of the dimer at equilibrium distance. Using the latter expression, express the avoided crossing term <math> B </math> as a function of the bonding energy of <math> H_{2}</math>.
| Answer
|
|
a - Considering the R and R* states for the radical exchange process, the HL wave functions for R and R* are the following :
<math>\psi (R)=(|xa\overline{y}|-|x\overline{a}y|)(1/2)^{-1/2} </math>
<math>\psi (R^{*})=(|x\overline{a}y|-|\overline{x}ay|)(1/2)^{-1/2}</math>
At the equilibrium distance of R, A and Y are close together while X is far away. Therefore R is stabilized by a covalent bond and its energy is <math> 2 \beta S </math>. In R*, the AY entity has two parallel spins 50% of the time (a repulsive situation), and alternated spins 50% of the time (a non-bonding situation). Therefore the energy of R* is half a triplet repulsion, i.e. <math> - \beta S </math>. As <math>\Delta E_{ST} (A-Y)= 4 \beta S </math>, the final G expression is:
<math>G=0.75 \Delta E_{ST} (A-Y)</math>
b - Let us express the various energies and matrix elements in terms of the usual <math> \beta </math> and <math> S </math> integrals between the X and H orbitals:
<math> E_{ind} = \beta S </math>
<math> S_{12} = 0.5 </math>
<math> H_{12} = 2 \beta S </math>
<math> RE = (2 \beta S - 0.5 \beta S )/1.5 = \beta S </math>
Since at the transition state geometry <math>\Delta E_{ST} </math>' = <math> 4 \beta S </math>, we have:
<math>B = 0.25\Delta E_{ST} </math>'
c - Since <math>\Delta E_{ST} </math>' <math> = 2 BDE </math>, we may re-express the avoided crossing term as:
<math>B = 0.5BDE </math>
|
2/ Computer exercise
VBSCD for H—H + H. -> H. + H—H at VBSCF then VBCISD level.
In this exercise the VBSCD for H—H + H. -> H. + H—H at VBSCF then VBCISD level will be computed with 6-31G**. Computations for reactant and transition state are requested and other points are optional for advanced users.
2.1 Computations
Compute the Energies and Wavefunctions at Reactant and Transition State with Different Sets of VB Structures
- Write the following VB structure sets, compare and see the difference:
- all structures;
- minimal structures for reactant;
- minimal structures for product.
- Perform VBSCF and VBCISD calculations for reactant:
- Perform a VBSCF calculation (file name: rs_vbscf) with "orbtyp=hao" and "boys";
- Perform a VBCISD calculation (file name: rs_vbcisd) with VBSCF orbital as initial guess.
- Perform VBSCF and VBCISD calculations with minimal structures for reactant (file names: rs_*_rs) and product (file names: rs_*_ps).
- Perform VBSCF and VBCISD calculations for transition state (file names: ts_*) with the same procedure as in step 2.
2.2 Analysis: Wavefunctions and Energies
- Compute the Barrier height of the <math>\textrm{S}_{\textrm{N}}2</math> reaction at VBSCF and VBCISD levels. See the difference of the barrier heights.
- Compare the energies for reactant and product structures at reactant and transition state, by both VBSCF and VBCISD. What's the difference of the energies at different points? Why?
- Compute the resonance energies at both reactant and transition state points, see the difference of the resonance energies.
2.3 Optional : Compute all points and draw the VBSCDs at VBSCF and VBCISD levels.
| Answer
|
|
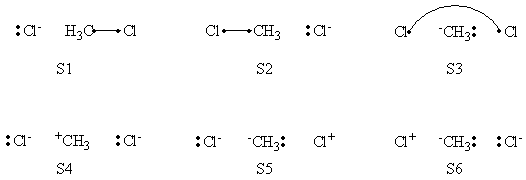
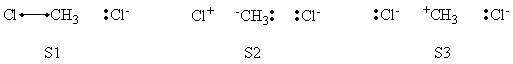
a- VB Structures used in the computations
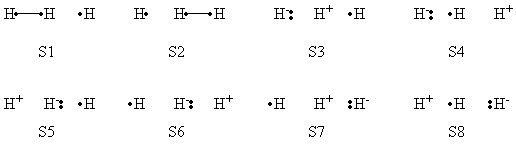
Total 8 Structures of The System
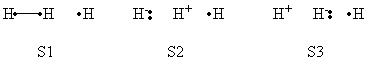
Structures of The Reactant State
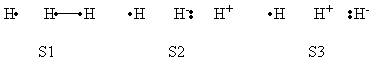
Structures of The Product State
b- Computational results
Weights of VB Structures of H-H-H Abstract Reaction at Reactant Geometry
|
|
S1
|
S2
|
S3
|
S4
|
S5
|
S6
|
S7
|
S8
|
| VBSCF
|
0.803 |
0.003 |
0.096 |
0.001 |
0.095 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000
|
| VBCISD
|
0.770 |
0.005 |
0.110 |
0.003 |
0.111 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.001
|
Weights of VB Structures of H-H-H Abstract Reaction at Transition State Geometry
|
|
S1
|
S2
|
S3
|
S4
|
S5
|
S6
|
S7
|
S8
|
| VBSCF
|
0.344 |
0.344 |
0.096 |
0.035 |
0.025 |
0.025 |
0.096 |
0.035
|
| VBCISD
|
0.358 |
0.358 |
0.059 |
0.036 |
0.046 |
0.046 |
0.059 |
0.036
|
Energies (a.u.) and Barriers (kcal/mol) of H-H-H Abstract Reaction
|
|
VBSCF
|
VBCISD
|
| Reactant
|
-1.64637 |
-1.66241
|
| Transition State
|
-1.60706 |
-1.63827
|
| Barrier
|
24.7 |
15.1
|
Energies(a.u.) and Resonance Energies (B, in kcal/mol) of H-H-H Abstract Reaction at Reactant Geometry
|
|
VBSCF
|
VBCISD
|
| All Structures
|
-1.64637 |
-1.66241
|
| Reactant
|
-1.64617 |
-1.66208
|
| Product
|
-1.40873 |
-1.41851
|
| B
|
0.1 |
0.2
|
Energies (a.u.) and Resonance Energies (B, in kcal/mol) of H-H-H Abstract Reaction at Transition State Geometry
|
|
VBSCF
|
VBCISD
|
| All Structures
|
-1.60706 |
-1.63827
|
| Reactant
|
-1.54798 |
-1.56655
|
| Product
|
-1.54798 |
-1.56655
|
| B
|
37.1 |
45.0
|
Optional : VBSCDs for H-H-H abstract reaction by VBSCF and VBCISD
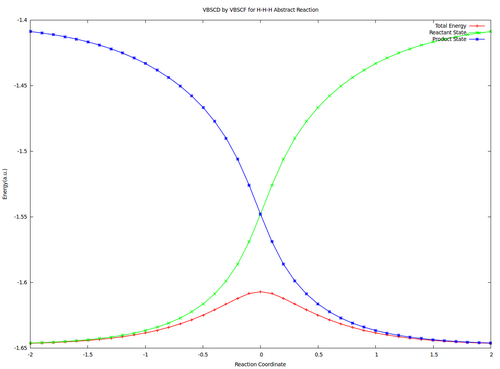 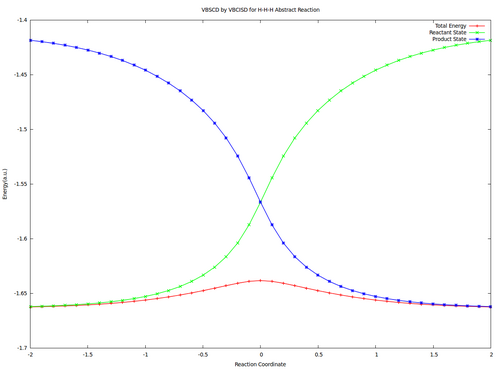
VBSCF VBCISD
|
Exercise 3 (paper exercise) : Conical intersection in H3• radical
(for further reading, see S. Shaik and P.C. Hiberty, "The Chemist's Guide to VB theory", Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2008, pp. 157-161, exercises 6.11-6.14 pp. 174-176, and answers to the exercises pp. 188-192.
Consider three hydrogen atoms Ha, Hb, Hc, with respective atomic orbitals a, b and c, and the two VB structures 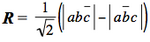 ] and ] and 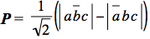 ] . ] .
The Ha-Hb and Hb-Hc distances are equal. 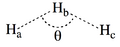
- By using the thumb rules recalled below, where squared overlap terms are neglected, derive the expression of the energies of R and P, and of the reduced Hamiltonian matrix element between R and P for the 3-orbital/3-electrons reacting system [Ha--Hb--Hc]•.
- From the sign of this latter integral when θ > 60°, derive the expressions of the ground state Ψ≠ and of the first excited state Ψ* of the H3• system. One may drop the normalization constants for simplicity. What bonding scheme does the excited state represent ?
- Show that the reduced Hamiltonian matrix element is largest in the collinear transition state geometry, and drops to zero in the equilateral triangular structure.
- Show that R and P VB structures are degenerate in the equilateral triangular structure, and that Ψ≠ and Ψ* are also degenerate in this geometry.
- We now extend the above conclusions to the allyl radical. What are the bonding schemes corresponding to the ground state and first excited state ? What geometrical distortion would make these two states degenerate ? What would be the end product of a photochemical excitation of allyl radical to its first excited state ?
Appendix : Thumb rules for the calculations of effective Hamiltonian matrix elements between determinants.
- Energy of a determinant D : <math><D|H|D> = -2 \sum_{i<j}^{ } \beta_{ij} S_{ij}</math> (if orbitals i and j have parallel spins)
- Matrix element between determinants differing by spin inversion of two spin-orbitals :
<math> <D|H|D'>=<|...i\overline{j}...||H||...\overline{i}j...|>= -2 \beta_{ij} S_{ij}</math> (for <math>D</math>, <math>D'</math> differing by spin inversion of two spin-orbitals)
| Answer
|
|
<math> R = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} (|ab\overline{c}|-|a\overline{b}c|) </math>
<math> P = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} (|a\overline{b}c|-|\overline{a}bc|) </math>
1 - Using the thumb rules
<math> <D|H|D>= -2 \sum_{i<j}^{ } \beta_{ij} S_{ij} </math>(if orbitals i and j have parallel spins)
<math> <D|H|D'>=<|...i\overline{j}...||H||...\overline{i}j...|>= -2 \beta_{ij} S_{ij} </math>(for D, D' differing by spin inversion of two spin-orbitals
It comes,
<math> <R|H|R>= \frac{1}{2} (4\beta_{bc}S_{bc} -2\beta_{ab}S_{ab} -2\beta_{ac}S_{ac})</math>
<math> <P|H|P>= \frac{1}{2} (4\beta_{ab}S_{ab} -2\beta_{bc}S_{bc} -2\beta_{ac}S_{ac})</math>
<math> <R|H|P>= \frac{1}{2} (4\beta_{ac}S_{ac} -2\beta_{ab}S_{ab} -2\beta_{bc}S_{bc})</math>
2 - If <math>\theta </math> > 60° , <math>\beta_{ac}S_{ac} < \beta_{ab}S_{ab}=\beta_{bc}S_{bc} </math> Hence <math><R|H|P> > 0 </math> (<math>\beta_{ij} < 0</math>)
Finally, ground state is out of phase and the excited state is in phase.
It comes:
- <math> \Psi^{\neq} = R-P</math>
- <math> \Psi^{\star} = R+P</math>
Expanding on the determinants
- <math> \Psi^{\neq} = 1/\sqrt{2} (|ab\overline{c}|+|\overline{a}bc|-2|a\overline{b}c|)</math>
- <math> \Psi^{\star} =1/\sqrt{2} (|ab\overline{c}|-|\overline{a}bc|)</math>
<math> \Psi^{\star} </math>, wave function of the excited state represent a bonding between hydrogens a and c.
3- Using geometric considerations
- If <math>\theta </math> = 180° , <math>\beta_{ac}S_{ac}=0</math> and <math> <R|H|P>=-(\beta_{ab}S_{ab} +\beta_{bc}S_{bc})</math>
- If <math>\theta </math> = 60° , <math>\beta_{ac}S_{ac}=\beta_{ab}S_{ab}=\beta_{bc}S_{bc}=\beta S</math> and <math> <R|H|P>=0</math>
4- If <math>\theta </math> = 60°, <math> <R|H|P>=0 = <R|H|R>= <P|H|P></math>
Hence R and P are degenerated eigenfunction of the CI Hamiltonian : <math>E_R=E_P=0</math>
Their linear combination <math> \Psi^{\neq} </math> and <math>\Psi^{\star} </math> are also degenerated, with the same value.
5- Allyl radical <math>\pi</math> system is isoelectronic to the <math>H_3</math> radical case.
R corresponds to the covalent right coupling (radical on the left carbone atom). P to the covalent right coupling.
- <math> \Psi^{\neq} </math> corresponds to the resonance (mesomery) between these 2 bonding schemes.
- <math>\Psi^{\star} </math> to the "through space" (a,c) electronic coupling ("long bond", the radical is centered on the middle atom).
The geometrical distortion to make the two states degenerated in allyl radical would be a rotation of the two CH2 end groups: by such a rotation, the resonance structures are destabilized (pi bonds break), and the a-c coupling is re-inforced (sigma bond forms).
The end product obtained from the first excited state of allyl radical is a cyclopropyl radical (formation of the a-c bond).
|
|