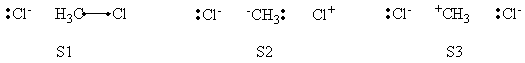Différences entre les versions de « VBTutorial3 »
| Ligne 397 : | Ligne 397 : | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | <big>'''Computations'''</big> | + | <big>'''2.1 Computations'''</big> |
Compute the Energies and Wavefunctions at Reactant and Transition State with Different Sets of VB Structures | Compute the Energies and Wavefunctions at Reactant and Transition State with Different Sets of VB Structures | ||
| Ligne 412 : | Ligne 412 : | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | <big>'''Analysis: Wavefunctions and Energies'''</big> | + | <big>'''2.2 Analysis: Wavefunctions and Energies'''</big> |
<br> | <br> | ||
# Compute the Barrier height of the <math>\textrm{S}_{\textrm{N}}2</math> reaction at VBSCF and VBCISD levels. See the difference of the barrier heights. | # Compute the Barrier height of the <math>\textrm{S}_{\textrm{N}}2</math> reaction at VBSCF and VBCISD levels. See the difference of the barrier heights. | ||
| Ligne 419 : | Ligne 419 : | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | <big>'''Optional : Compute all points and draw the VBSCDs at VBSCF and VBCISD levels.'''</big> | + | <big>'''2.3 Optional : Compute all points and draw the VBSCDs at VBSCF and VBCISD levels.'''</big> |
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | | class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !<big>'''BLW within GAMESS (Version: MAR-25-2010 R2)'''</big> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | a- VB Structures used in the computations | ||
| + | <center>[[File:Structures.png|600px]] </center><br> | ||
| + | <center>Total 8 Structures of The System</center> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <center>[[File:Reactant_Structures.png|400px]] </center><br> | ||
| + | <center>Structures of The Reactant State</center> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <center>[[File:Product_Structures.png|400px]] </center><br> | ||
| + | <center>Structures of The Product State</center> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | b- Computational results | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | {| border="1" | ||
| + | |+ Weights of VB Structures of H-H-H Abstract Reaction at Reactant Geometry | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S1 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S2 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S3 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S4 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S5 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S6 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S7 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S8 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | VBSCF | ||
| + | | 0.803 || 0.003 || 0.096 || 0.001 || 0.095 || 0.000 || 0.000 || 0.000 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | VBCISD | ||
| + | | 0.770 || 0.005 || 0.110 || 0.003 || 0.111 || 0.000 || 0.000 || 0.001 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | {| border="1" | ||
| + | |+ Weights of VB Structures of H-H-H Abstract Reaction at Transition State Geometry | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S1 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S2 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S3 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S4 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S5 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S6 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S7 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | S8 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | VBSCF | ||
| + | | 0.344 || 0.344 || 0.096 || 0.035 || 0.025 || 0.025 || 0.096 || 0.035 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | VBCISD | ||
| + | | 0.358 || 0.358 || 0.059 || 0.036 || 0.046 || 0.046 || 0.059 || 0.036 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | {| border="1" | ||
| + | |+ Energies (a.u.) and Barriers (kcal/mol) of H-H-H Abstract Reaction | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | VBSCF | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | VBCISD | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" |Reactant | ||
| + | | -1.64637 || -1.66241 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Transition State | ||
| + | | -1.60706 || -1.63827 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Barrier | ||
| + | | 24.7 || 15.1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | {| border="1" | ||
| + | |+ Energies(a.u.) and Resonance Energies (''B'', in kcal/mol) of H-H-H Abstract Reaction at Reactant Geometry | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | VBSCF | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | VBCISD | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | All Structures | ||
| + | | -1.64637 || -1.66241 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Reactant | ||
| + | | -1.64617 || -1.66208 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Product | ||
| + | | -1.40873 || -1.41851 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | ''B'' | ||
| + | | 0.1 || 0.2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | {| border="1" | ||
| + | |+ Energies (a.u.) and Resonance Energies (''B'', in kcal/mol) of H-H-H Abstract Reaction at Transition State Geometry | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | VBSCF | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | VBCISD | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | All Structures | ||
| + | | -1.60706 || -1.63827 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Reactant | ||
| + | | -1.54798 || -1.56655 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | Product | ||
| + | | -1.54798 || -1.56655 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="row" | ''B'' | ||
| + | | 37.1 || 45.0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
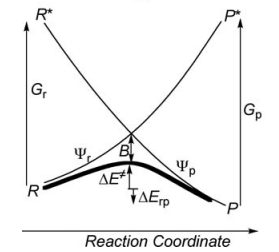
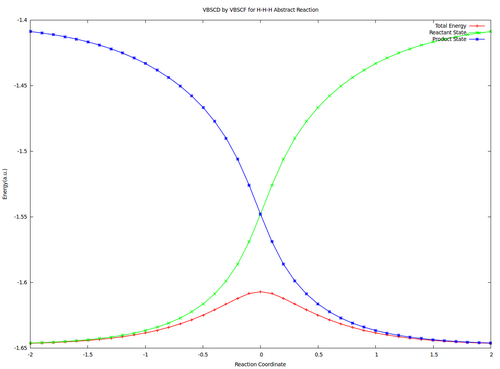
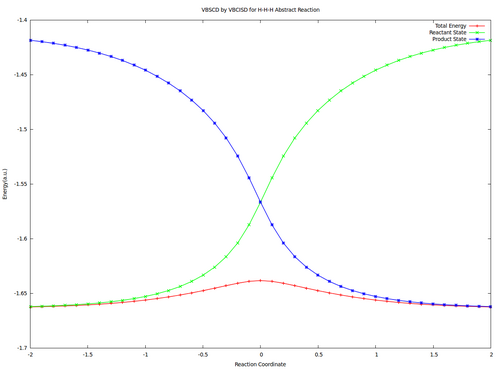
| + | <center><big>Optional : VBSCDs for H-H-H abstract reaction by VBSCF and VBCISD</big></center> | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[File:H3-VBSCD-VBSCF.png|500px]] [[File:H3-VBSCD-VBCISD.png|500px]]<br> |
| + | <big> {{pad|250px}} VBSCF {{pad|420px}} VBCISD </big> | ||
| + | |} | ||
== Exercise 3 (paper exercise) : Conical intersection in H<sub>3</sub><sup>•</sup> radical == | == Exercise 3 (paper exercise) : Conical intersection in H<sub>3</sub><sup>•</sup> radical == | ||
Version du 12 juillet 2012 à 12:04
Valence Bond State correlation diagrams
Exercise 1 : Computation of state correlation Diagrams for a 3 centers / 4 electrons system
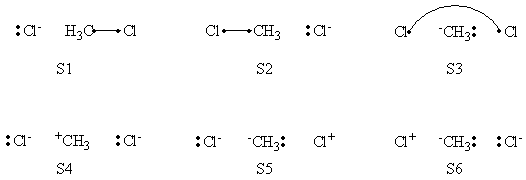
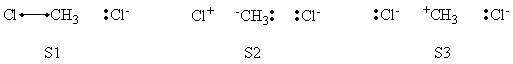
In this exercise the <math>\textrm{S}_{\textrm{N}}2</math> reaction Cl<math>{}^{-}</math> + CH3Cl -> ClCH3 + Cl<math>{}^{-}</math> will be studied in both vacuum and solution. Valence Bond State Correlation Diagrams (VBSCD) will be constructed at <math>\pi</math>-D-BOVB level. There are two parts in this exercise: basic part and optional part. The basic part is performed with MCP-DZP basis set in which the inner orbitals in Cl and C are described with MCP pseudo potential. The optional part is performed with 6-31+G* basis set, using the general specification for the xmvb input (expert users). Only reactant and transition state will be computed in this exercise, which is sufficient to build the VBSCD diagrams.
| Note:How to perform a VBPCM calculation |
|---|
|
A VBPCM calculation is performed in the similar way as the VB calculations in vacuum. One should prepare a GAMESS input file with solvent assigned such as: The details of PCM calculation in the GAMESS can be found in GAMESS manual. Keyword "VBTYP=XMVB" in CONTRL section is also essential. After the GAMESS input file is prepared, an XMI file with keyword "VBPCM" should be prepared with the same file name as GAMESS input file. In the current XMVB package, VBSCF/PCM and BOVB/PCM calculations are both supported. |
| Basic part |
|---|
1. Compute the Energies and Wavefunctions at Reactant and Transition State with Different Sets of VB Structures
2. Analysis: Wavefunctions and Energies
|
| Optional part (expert users) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
In this part, calculations with BFI section are performed with 6-31+G* basis set, which is desired for the experienced users. The inner orbitals are frozen as HF orbitals in all VB calculations and the valence basis functions are reorganized to hybrid basis functions so that the <math>\sigma</math>, <math>\pi_x</math> and <math>\pi_y</math> spaces can be separated well. A D-BOVB calculation is performed in 2 steps:
The VB calculations are the same as the calculations performed above. Try to understand the BFI section, perform the calculations and compare the differences of barrier heights, resonance energies and performances with and without $BFI.
|
>> general guidelines for BOVB calculations
| Optional exercises - Homework | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Exercise 2 : computation of H—H + H. -> H. + H—H radical exchange VBSCD diagram1/ Paper exercise :a/ Considering the following radical exchange process: <math> X^{\bullet} + A-Y \rightarrow X-A + ^{\bullet}Y </math> (X = A = Y = hydrogen atom) Write the HL wave functions for R and R* and derive the value of G using semiempirical VB theory. Hints : 1) write the wave functions of R and R* so that their overlap is positive; 2) neglect the overlap beween the external atoms X and Y, and neglect the overlap between two different determinants. b/ Considering the following reaction:
<math>
X^{\bullet} + H-X \rightarrow X-H +^{\bullet}X
</math> <math>RE = [H_{12}-E_{ind}S_{12}]/(1+S_{12}) </math> where <math> E_{ind} </math> is the energy of an individual VB structure, and <math> S_{12} </math> and <math> H_{12} </math> are respectively the overlap and Hamiltonian matrix element between R and R*. c/ It is known that for strong binders, at any given bonding distance the singlet-triplet transition energy is larger than twice the bonding energy of the dimer at equilibrium distance, so that one can write the approximate expression <math>\Delta E_{ST} </math>' <math> = 2 BDE </math>, where <math> BDE </math> is the bonding energy of the dimer at equilibrium distance. Using the latter expression, express the avoided crossing term <math> B </math> as a function of the bonding energy of <math> H_{2}</math>.
2/ Computer exerciseVBSCD for H—H + H. -> H. + H—H at VBSCF then VBCISD level. In this exercise the VBSCD for H—H + H. -> H. + H—H at VBSCF then VBCISD level will be computed with 6-31G**. Computations for reactant and transition state are requested and other points are optional for advanced users.
Compute the Energies and Wavefunctions at Reactant and Transition State with Different Sets of VB Structures
|
class="collapsible collapsed wikitable" | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BLW within GAMESS (Version: MAR-25-2010 R2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a- VB Structures used in the computations 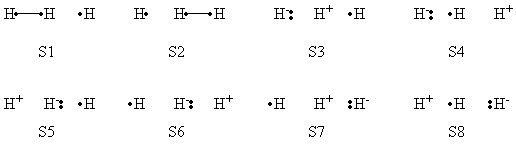
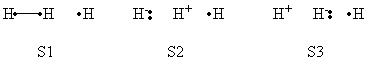
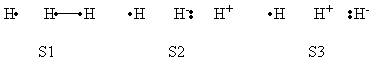
|
Exercise 3 (paper exercise) : Conical intersection in H3• radical
(for further reading, see S. Shaik and P.C. Hiberty, "The Chemist's Guide to VB theory", Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2008, pp. 157-161, exercises 6.11-6.14 pp. 174-176, and answers to the exercises pp. 188-192.
Consider three hydrogen atoms Ha, Hb, Hc, with respective atomic orbitals a, b and c, and the two VB structures ![]() ] and
] and ![]() ] .
] .
The Ha-Hb and Hb-Hc distances are equal. ![]()
- By using the thumb rules recalled below, where squared overlap terms are neglected, derive the expression of the energies of R and P, and of the reduced Hamiltonian matrix element between R and P for the 3-orbital/3-electrons reacting system [Ha--Hb--Hc]•.
- From the sign of this latter integral when θ > 60°, derive the expressions of the ground state Ψ≠ and of the first excited state Ψ* of the H3• system. One may drop the normalization constants for simplicity. What bonding scheme does the excited state represent ?
- Show that the reduced Hamiltonian matrix element is largest in the collinear transition state geometry, and drops to zero in the equilateral triangular structure.
- Show that R and P VB structures are degenerate in the equilateral triangular structure, and that Ψ≠ and Ψ* are also degenerate in this geometry.
- We now extend the above conclusions to the allyl radical. What are the bonding schemes corresponding to the ground state and first excited state ? What geometrical distortion would make these two states degenerate ? What would be the end product of a photochemical excitation of allyl radical to its first excited state ?
Appendix : Thumb rules for the calculations of effective Hamiltonian matrix elements between determinants.
- Energy of a determinant D : <math><D|H|D> = -2 \sum_{i<j}^{ } \beta_{ij} S_{ij}</math> (if orbitals i and j have parallel spins)
- Matrix element between determinants differing by spin inversion of two spin-orbitals :
<math> <D|H|D'>=<|...i\overline{j}...||H||...\overline{i}j...|>= -2 \beta_{ij} S_{ij}</math> (for <math>D</math>, <math>D'</math> differing by spin inversion of two spin-orbitals)
|}