VBTutorial3
How to modify this page :
- first : log in (top right of this page) ;
- click on [edit] (far right) to edit a section of the page ;
- write your text directly in the wiki page, and click on the "Save page" button (bottom left) to save your modifications
Pictures : how to insert a picture in your text
See also this page for an introduction to the basics of the wiki syntax
Remarks
Exercices
Exercice 1 (paper exercice) : Conical intersection in H3• radical
(for further reading, see S. Shaik and P.C. Hiberty, "The Chemist's Guide to VB theory", Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2008, pp. 157-161, exercises 6.11-6.14 pp. 174-176, and answers to the exercises pp. 188-192.
Consider three hydrogen atoms Ha, Hb, Hc, with respective atomic orbitals a, b and c, and the two VB structures ![]() ] and
] and ![]() ] .
] .
The Ha-Hb and Hb-Hc distances are equal. ![]()
- By using the thumb rules recalled below, where squared overlap terms are neglected, derive the expression of the energies of R and P, and of the reduced Hamiltonian matrix element between R and P for the 3-orbital/3-electrons reacting system [Ha--Hb--Hc]•.
- From the sign of this latter integral when θ > 60°, derive the expressions of the ground state Ψ≠ and of the first excited state Ψ* of the H3• system. One may drop the normalization constants for simplicity. What bonding scheme does the excited state represent ?
- Show that the reduced Hamiltonian matrix element is largest in the collinear transition state geometry, and drops to zero in the equilateral triangular structure.
- Show that R and P VB structures are degenerate in the equilateral triangular structure, and that Ψ≠ and Ψ* are also degenerate in this geometry.
- We now extend the above conclusions to the allyl radical. What are the bonding schemes corresponding to the ground state and first excited state ? What geometrical distortion would make these two states degenerate ? What would be the end product of a photochemical excitation of allyl radical to its first excited state ?
Appendix : Thumb rules for the calculations of effective Hamiltonian matrix elements between determinants.
- Energy of a determinant D :
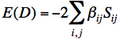 ] (if orbitals i and j have parallel spins)
] (if orbitals i and j have parallel spins) - Matrix element between determinants differing by spin inversion of two spin-orbitals :
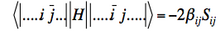 ]
]
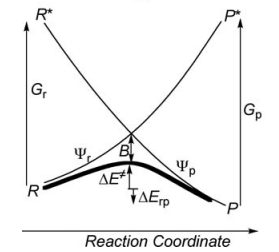
Exercice 2 : computation of X—X + X. -> X. + X—X radical exchange VBSCD diagram for X=H,Li
- Paper exercice :
- Beginning of ex. 6.3 from Sason & Philippe's book (first 3 lines)
Considering the reactant (R) and product (R*) in the following radical exchange process: <math> X\cdot + A-Y \rightarrow X-A + \cdotY </math> Write the HL wave functions for R and R* and derive the value of G using semiempirical VB theory.
- Exercice 6.5 from Sason & Philippe's book
- Exercice 6.6 questions a),b) and c)
- Exercice 6.6 question d)
- Exercice 6.6 question e)
- Computer exercise :
idea : Compute VBSCD diagrams for X—X + X. -> X. + X—X X=H, Li at VBSCF then VBCI level. To be written...
Exercice 3 : Computation of state correlation Diagrams for a 3 centers / 4 electrons system
Sason's remark :
" F(-) + H-F example is not good by itself, unless you also do F• + H-F - showing that in one case you have an intermediate FHF(-) and in the other case you have a high barrier.
If we just want to do one case of 4-electron/3-center reaction, we should use Cl(-) + CH3Cl.
The audience will appreciate a more chemical example, which is Cl(-) + CH3Cl. "
Benoît's proposition :
- Paper exercice :
- Exercice 6.12 question a) (from Sason & Philippe's book)
- Exercice 6.12 question b)
- Computer exercise :
idea : Compute VBSCD diagrams for Cl(-) + CH3Cl -> ClCH3 + Cl(-), at D-BOVB levels, first in gas phase then using VB(PCM)... Which basis set should we use : 6-31+G*. As this is an anion we should add a set of diffuse functions, but then there may be trouble with BOVB... Check first that everything is fine at BOVB level (no instability)...