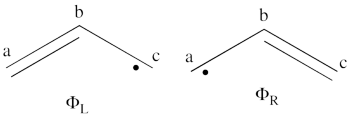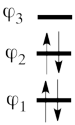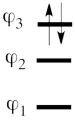Exercise 1 : The allyl radical
| Paper exercise
|
- Covalent structures of the allyl radical :
- What are the three possible covalent structures for the allyl radical molecule ? Use the thumb rules of qualitative VB theory to compute their energy, and show that two of them are degenerate.
- Show that the third structure can be expressed as a linear combination of the first two structures, and thus that only two of the three covalent structures form a complete basis of non-redundant structures (Rumer basis).
- Understanding the pattern of spin density distributions in the allyl radical as found in EPR spectroscpy.
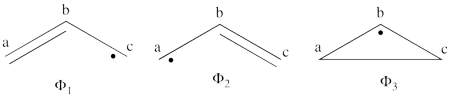
- Express the wave functions of the non-redundant structures (from 1.1) of allyl radical in terms of the VB determinant. Write the wave function of the ground state of the allyl radical as a negative combination of the wave functions of the non-redundant structures. Based on the expression of the spin density <math> \rho_s </math>
<math> {\rho_k}^s = N^2 \sum_i {c_i}^2 {\delta_{ki}}</math>
propose the spin density distribution in the allyl radical. In the above equation N is a normalization constant, c is the coefficient of the VB determinant in the wave function and <math> \delta </math> is either +1 or -1 depending on whether the electron which is located on atom k in the ith determinant is <math> \alpha </math> or <math> \beta </math> spin, respectively.
- Show pictorially:
- Why your spin density is polarized.
- What would be the spin density pattern in pentadienyl radical?
- What would be the spin density in the excited state of allyl radical (taking into account that resulting wave function is a positive combination of the <math> \Phi_L </math> and <math> \Phi_R </math> wave functions?
- Covalent and ionic structures of the allyl radical :
- What are the possible ionic structures for the allyl radical ? Based on your chemical knowledge, propose a selection subset of the most chemically meaningful covalent + ionic structures.
| Answer
|
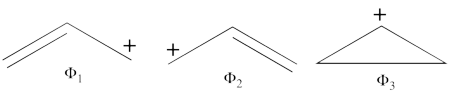
1. Covalent structures of the allyl radical:
- The following are the three possible covalent structures:
According to the thumb rules of qualitative VB theory (given in lecture I), both <math> \Phi_1 </math> and <math> \Phi_2 </math> display an unpaired electron in the vicinity of one end of a covalent bond. The energy for this repulsion is <math> -\beta</math>S, while the energy of the covalent bond is <math> 2\beta</math>S. Therefore, the total energy for either <math> \Phi_1 </math> or <math> \Phi_2 </math> is <math> \beta</math>S. For <math> \Phi_3 </math>, the unpaired electron is in the vicinity of both ends of the covalent bond, therefore the corresponding repulsion is twice <math> -\beta</math>S. As for the energy of the covalent bond, it can be neglected since it is a "long" bond, between atoms that are not neighbors. So the total energy for <math> \Phi_3 </math> is <math> -2\beta</math>S.
- <math>
\Phi_{\textrm{1}} = \vert a\bar{b}c\vert - \vert \bar{a}bc\vert
</math>
<math>
\Phi_2 = \vert ab\bar{c}\vert - \vert a\bar{b}c\vert
</math>
<math>
\Phi_3 = \vert ab\bar{c}\vert - \vert \bar{a}bc\vert = \Phi_1 + \Phi_2
</math>
Since <math> \Phi_{\textrm{3}} </math> is the positive combination of <math> \Phi_{\textrm{1}} </math> and <math> \Phi_{\textrm{2}} </math> the two first structures form a complete basis of non-redundant structures.
2.Understanding the pattern of spin density distributions in the allyl radical as found in EPR spectroscopy
- The wave functions of the non-redundant structures are
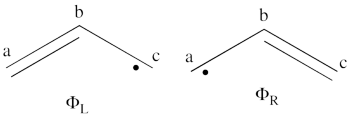
<math>
\Phi_L = \frac{1}{\sqrt2}[\vert a\bar{b}c\vert - \vert \bar{a}bc\vert]
</math>
<math>
\Phi_R = \frac{1}{\sqrt2}[\vert ab\bar{c}\vert - \vert a\bar{b}c\vert]
</math>
The negative combination of these two wave functions determines the ground state wave-function of allyl radical
<math>
\Phi_{GS}= \Phi_L - \Phi_R= \frac{1}{\sqrt6}[2\vert a\bar{b}c\vert - \vert \bar{a}bc\vert -
\vert ab\bar{c}\vert]
</math>
We note with that respect that the determinant with the largest coefficient in the ground state is the spin-alternant determinant. We can see that the weight of this spin-alternant determinant is four times larger than the corresponding weights of the two other determinants. This, as we will show later can explain the polarization of the spin density.
Now, let's use the following expression for the spin density: <math>
\rho_k= N^2 \sum_i {c_i}^2 {\delta_{ki}}
</math> to calculate the spin density distribution in the allyl radical:
<math>
\rho_a = \frac{1}{6}[4 - 1 + 1] = \frac{2}{3}
</math>
<math>
\rho_b = \frac{1}{6}[-4 + 1 + 1] = -\frac{1}{3}
</math>
<math>
\rho_c = \frac{1}{6}[4 + 1 - 1] = \frac{2}{3}
</math>
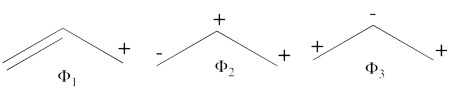
- Since <math> \Phi_{GS} </math> is dominated by the spin-alternant determinant <math> \vert a\bar{b}c\vert </math>, (as mentioned before, it has the largest coefficient in the ground state), the spin distribution properties could in fact be predicted without any calculation, but just by looking at the spin-alternant determinant.
- Here is a pictorial representation of the spin-alternant determinant. It is clear that it predicts spin polarization with a spin-down on the central carbon atom and spin-up on the two terminals. As such, (since it dominates the ground state wave-function) it is predicted that the ground state wave function will exhibit the same spin distribution. In other words, in principle, in this case it could be sufficient to look at this spin-alternant determinant to get a qualitative correct estimate of the spin distribution.
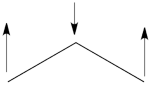
- The spin-alternant determinant will generally dominate the wave function of the ground state for the entire series of conjugated radicals. For example, if we wish to predict/understand the spin density patterns of the pentadienyl radical, all we have to do is draw the spin-alternant determinant. Thus, as shown below for pentadienyl the central carbon atom has spin up, and the spins alternate in direction on both sides.
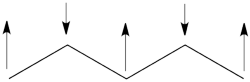
The next radical in line (with 7 carbons) will have a similar spin distribution as in allyl, with spin-down in the center flanked by spin-ups on both sides, etc.
- Lets turn now to the excited state of allyl radical. Since the ground state is the negative combination of the <math> \Phi_L </math> and <math> \Phi_R </math> structures above, the excited state is the corresponding positive combination. This positive combination eliminates the spin-alternant determinant, and we remain with: <math>
\Phi_{EXS} = \Phi_L + \Phi_R= \frac{1}{\sqrt2}[\vert ab\bar{c}\vert -\vert \bar{a}bc\vert ]
</math>
Pictorially, this is simply the cyclopropyl structure with spin density localized only on the central carbon:
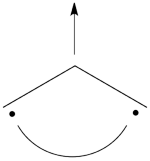
Note how the spin switches from the ground- to the excited state. It is generally true that in the first excited state of the polyenyl radicals, the spin alternant determinant vanishes and the spin density is determined by the long bond structures.
3. Covalent and ionic structures of the allyl radical:
- From each covalent structure we can get two ionic structures. Additional two ionic structures are obtained from the redundant structure. Therefore overall there are 6 different ionic structures
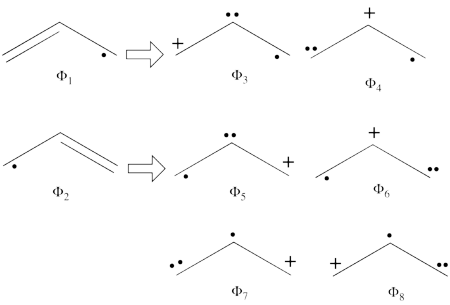
In the two ionic structures (<math> \Phi_{\textrm{7}} </math>,<math> \Phi_{\textrm{8}} </math>) that are based on the redundant structure the charges are farther from each other compared with the other ionic structures and are therefore, expected to be higher in energy. These two structures will therefore not be included in our chosen sub-set of structures.
|
|
| Computer Exercise
|
- Computation of covalent state of allyl radical
- Compute the VBSCF wave function for the covalent state of the allyl radical (6-31G* basis set) using the covalent structures you have chosen (paper Ex. 1.2). What are the weights of the different VB structures. Was that expected?
- What is the wavefunction in determinant description? What is the spin population? Do the calculated results agree with your answer for paper Ex. 2.1?
- Repeat the calculation for the first excited state using "nstate=1" . What is the the wavefunction? Use determinant description. What is the spin population in this case? Was that expected?
- Computation of allyl radical energy and weights:
- Compute a VBSCF wave function for allyl radical (6-31G* basis set) using your selected set of structures (questions 1.2 and 3.1). Compute a VBSCF wave function including the complete set of VB structures (the adiabatic wavefunction), using the "str=full" keyword. Compare the weights and energies for both wave functions to validate your selection of structures.
- Compute for allyl radical a BOVB wave function which includes only your selected set of most chemically meaningful structures (remember to use the guess orbitals obtained at the VBSCF level). Compare the weights obtained at the VBSCF and BOVB levels.
- Computation of resonance energies :
- We want to build a wave-function corresponding to only one Lewis (diabatic) structure for the allyl radical. To do so, we will include in the wave-function only one covalent structure, and the ionic structures associated with this covalent bond. Propose a selection of VB structures which would describe one Lewis structure for the allyl radical.
- Compute this wave function at VBSCF then BOVB levels. Deduce what is the resonance energy of the allyl radical at the BOVB level. The resonance energy is calculated as the difference between the adiabatic state and the Lewis (diabatic) state of the allyl radical.
| Answer
|
1. Computation of covalent state of allyl radical
- The weights of the two structures, <math> \Phi_1 </math> and <math> \Phi_{\textrm{2}} </math> is identical and equals 0.5 as expected.
- The wavefunction in determinant description is:
<math>
\psi_{GS}= -0.37\vert bc\bar{a}\vert - 0.78\vert ac\bar{b}\vert + 0.37\vert ba\bar{c}\vert
</math>
Rearrangement of the determinants results with the following wavefunction:
<math>
\psi_{GS}= 0.78\vert a\bar{b}c\vert - 0.37\vert \bar{a}bc\vert - 0.37\vert ab\bar{c}\vert
</math>
which is identical to the wavefunction derived in Paper Ex. 2.1.
Similarly, the spin pupolation obtained in the calculation is 0.667, -0.333, 0.667 for carbons a, b and c respectively in agreemnet with the results obtained in Paper Ex. 2.1.
- The wavefunction in the first excited state is:
<math>
\psi_{EX}= \Phi_1 + \Phi_2 = 0.71\vert bc\bar{a}\vert + 0.71\vert ba\bar{c}\vert
</math>
Again, rearrangement of the determinants results with the following wavefunction:
<math>
\psi_{GS}= 0.71\vert \bar{a}bc\vert - 0.71\vert ab\bar{c}\vert
</math>
and the corresponding spin population is: 1.0 on the central carbon as is expected for the long bond structure predicted in paper Ex. 2.3.
2. Computation of the allyl radical energies and weights
- The total energy of the VB wave function with selected set of structures
VB energies of the allyl radical
| Structures & Method
|
Total Energy (au)
|
| 2 cov + 4 ionic (VBSCF)
|
-116.37308766
|
| Str=full (VBSCF)
|
-116.37668662
|
| 2 cov + 4 ionic (BOVB)
|
-116.39521431
|
The energy difference is -2.25 kcal/mol within the VBSCF. Comparison of VBSCF with BOVB both only using the selected subset, one gets a difference of -13.88 kcal/mol
- Comparison of the weights of the VB wavefunction:
Weights of the VB structures of the allyl radical
|
|
Str=full (VBSCF)
|
2 cov + 4 ion (VBSCF)
|
2 cov + 4 ion (BOVB)
|
| <math>\phi_1</math> 1:10 11 12 13
|
0.36392 |
0.37056 |
0.32495
|
| <math> \phi_2 </math> 1:10 12 13 11
|
0.36392 |
0.37056 |
0.32495
|
| <math> \phi_3 </math> 1:10 12 12 13
|
0.05844 |
0.06257 |
0.08716
|
| <math>\phi_4 </math> 1:10 11 11 13
|
0.06454 |
0.06687 |
0.08789
|
| <math> \phi_5 </math> 1:10 12 12 11
|
0.05844 |
0.06257 |
0.08716
|
| <math> \phi_6 </math> 1:10 13 13 11
|
0.06454 |
0.06687 |
0.08789
|
| <math> \phi_7 </math> 1:10 11 11 12
|
0.01310
|
| <math> \phi_8 </math> 1:10 13 13 12
|
0.01310
|
When comparing 2 cov + 4 ion with Str=full we see that the weights of the last two structures in the second calculation (the more comprehensive calculation) are indeed very small.
3. Computation of resonance energies for the Allyl radical
- The following are the three structures of allyl radical which describe one of its Lewis structures (the structure which involves a bond between atoms a and b and an unpaired electron on atom c):
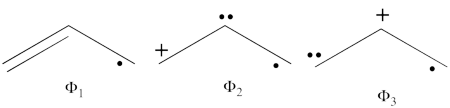
- The total energy of the VB wave function of this Lewis structure is summarized in the following table:
Total energies and weights of one of the Lewis structures of the allyl radical
|
|
VBSCF
|
BOVB
|
| Total energy (au)
|
-116.34255135 |
-116.359365
|
| weight of <math> \Phi_1 </math>
|
0.80496 |
0.73157
|
| weight of <math> \Phi_2 </math>
|
0.09494 |
0.13011
|
| weight of <math>\Phi_3 </math>
|
0.10010 |
0.13832
|
At the BOVB level, the resonance energy (RE) of the allyl radical which is the difference between the total energy of the allyl radical with full set of the structures and the total energy of the Lewis structure only is RE = 22.5 kcal/mol.
|
FILES FOR Exersice1
|
Exercise 2 : Radical character of ozone
| Computer exercise
|
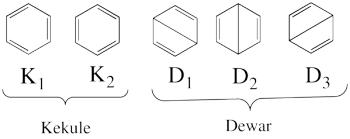
- Propose a complete basis of non-redundant VB structures for the ozone molecule. Based on your chemical knowledge, propose a selection subset of the most chemically meaningful structures. (Paper exercise)
- Compute a VBSCF wave function for ozone (6-31G basis set) using your selected set of structures. Compute a VBSCF wave function including the complete set of VB structures, using the "str=full" keyword. Compare the weights and energies for both wave functions to validate your selection of structures.
- Compute a BOVB wave function for ozone which includes only your selected set of most chemically meaningful structures (use the guess orbitals obtained at the VBSCF level).
- Compare the weights obtained at the VBSCF and BOVB level. Compare the BOVB diradical weight to the value predicted by simple MO theory. For your convenience the MO wave function is as follows
<math>
\psi_{H\ddot{u}ckel} =
25%\Phi_1 +
25%\Phi_2 + 12.5%\Phi_3 +
25%\Phi_4 + 6.25%\Phi_5 +
6.25%\Phi_6
</math>
(consult the following paper exercise)
| Anwser
|
- Complete set of the non-redundant VB structures of the ozone are
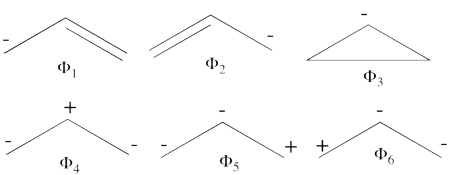
<math> \Phi_{\textrm{1}}= \frac{1}{\sqrt2}(\vert p_1\overline p_1p_2\overline p_3\vert + \vert p_1\overline p_1p_3\overline p_2\vert)
</math>
<math>
\Phi_{\textrm{2}}= \frac{1}{\sqrt2}(\vert p_3\overline p_3p_1\overline p_2\vert + \vert p_3\overline p_3p_2\overline p_1\vert)
</math>
<math>
\Phi_{\textrm{3}}= \frac{1}{\sqrt2}(\vert p_2\overline p_2p_1\overline p_3\vert + \vert p_2\overline p_2p_3\overline p_1\vert)
</math>
<math>
\Phi_{\textrm{4}}= \vert p_1\overline p_1p_3\overline p_3\vert
</math>
<math>
\Phi_{\textrm{5}}= \vert p_1\overline p_1p_2\overline p_2\vert
</math>
<math>
\Phi_{\textrm{6}}= \vert p_2\overline p_2p_3\overline p_3\vert
</math>
The structures <math> \Phi_{\textrm{5}}</math> and <math> \Phi_{\textrm{6}}</math> are expected to be high on energy and therefore will not be included in our chosen sub-set of structures.
Answer for 2-4:
- The total energy of the VB wave function of ozone is summarized in the following Table:
VB energies of the ozone
| Structures & Method
|
Total Energy (au)
|
| 3 cov + 1 ionic (VBSCF)
|
-224.22969470
|
| Str=full (VBSCF)
|
-224.23481239
|
| 3 cov + 1 ionic (BOVB)
|
-224.29172132
|
The energy difference is -2.25 kcal/mol within the VBSCF. Comparison of VBSCF with BOVB both only using the selected subset, one gets a difference of -13.88 kcal/mol
- The weights of the VB wave function of ozone are summarized in the following Table:
Weights of the VB structures of the ozone
|
|
Str=full (VBSCF)
|
3 cov + 1 ion (VBSCF)
|
3 cov + 1 ion (BOVB)
|
| <math>\phi_1</math> 1:10 11 11 12 13
|
0.15232 |
0.14942 |
0.23026
|
| <math> \phi_2 </math> 1:10 13 13 11 12
|
0.15232 |
0.14942 |
0.23026
|
| <math> \phi_3 </math> 1:10 12 12 11 13
|
0.66330 |
0.68922 |
0.47772
|
| <math>\phi_4 </math> 1:10 11 11 13 13
|
0.01279 |
0.01195 |
0.06177
|
| <math> \phi_5 </math> 1:10 11 11 12 12
|
0.00963
|
| <math> \phi_6 </math> 1:10 12 12 13 13
|
0.00963
|
Thus, according to the BOVB calculation the radical character of ozone is significant, 48% (!) compared to only 12.5% within simplified MO (see solution for paper exercise below).
|
FILES FOR Exercise2
|
| Paper Exercises - Homework
|
- Use the HuLis software to retrieve the Hückel MOs for ozone. Write a single-determinant MO wave function based on Hückel orbitals. Develop it into the basis of atomic orbitals, to get an expression in terms of VB structures (consult the hint given below).
- Compute by hand the weights of the different structures (neglecting all overlaps for simplicity). What is the radical character of ozone according to simple MO theory?
| Answer
|
- The MO orbitals in the Huckel approximation for ozone are:
<math>
\varphi_1 = \frac{1}{2}(p_1 + \sqrt{2}p_2 + p_3) </math>
<math>
\varphi_2 = \frac{1}{\sqrt2}(p_1 - p_3)</math>
<math>
\varphi_3 = \frac{1}{2}(p_1 - \sqrt{2}p_2 + p_3)
</math>
A single-determinant MO wavefunction of ozone based on these Hückel orbitals would look as follows:
<math>
\psi_{H\ddot{u}ckel} = \vert \varphi_1\bar{\varphi_1}\varphi_2\bar{\varphi_2}\vert =
\vert [\frac{1}{2}(p_1 + \sqrt{2}p_2 + p_3)][\overline{\frac{1}{2}(p_1 + \sqrt{2}p_2 + p_3)]}[\frac{1}{\sqrt2}(p_1 - p_3)][\overline{\frac{1}{\sqrt2}(p_1 - p_3)]} \vert
</math>
However, we can simplify the problem by using the electron/hole equivalence: >> the electron-hole equivalence
Thus, we simply replace holes by electrons and vise versa in <math> \psi_{H\ddot{u}ckel} </math> getting a function of <math> {\psi_{H\ddot{u}ckel}}^{hole} </math>, which we will then expande in terms of VB structures. Finally, we will perform the back hole-electron transformation in the VB representation to get the final result. This way we transform a 4e-3c problem into 2h-3c one.
<math>
{\psi_{H\ddot{u}ckel}}^{hole} = \vert \varphi_3\bar{\varphi_3}\vert = \frac{1}{4} \vert (p_1 - \sqrt{2}p_2 + p_3)\overline{(p_1 - \sqrt{2}p_2 + p_3)} \vert
</math>
Expanding into AO determinants, we get:
<math>
{\psi_{H\ddot{u}ckel}}^{hole} = \frac{1}{4} (\vert (p_1\overline p_3 \vert + \vert (p_3\overline p_1 \vert) - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{4}(\vert p_1\overline p_2 \vert + \vert p_2 \overline p_1 \vert) - \frac{\sqrt{2}}{4}(\vert p_2\overline p_3 \vert + \vert p_3 \overline p_2 \vert) + \frac{1}{4} \vert p_1\overline p_1 \vert + \frac{1}{4} \vert p_3\overline p_3 \vert + \frac{1}{2} \vert p_2\overline p_2 \vert
</math>
Doing the electron-hole back transformation, we get:
<math>
\psi_{H\ddot{u}ckel} = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{4}\Phi_3 - \frac{1}{2}\Phi_1 - \frac{1}{2}\Phi_2 + \frac{1}{4}\Phi_6 + \frac{1}{4}\Phi_5 + \frac{1}{4}\Phi_4
</math>
- The corresponding weights while neglecting overlap (for simplicity) are therefore:
<math>
\psi_{H\ddot{u}ckel} =
25%\Phi_1 +
25%\Phi_2 + 12.5%\Phi_3 +
25%\Phi_4 + 6.25%\Phi_5 +
6.25%\Phi_6
</math>
Thus, according to simple MO theory the radical character of ozone is 12.5%.
|
| Hint
|
|
- It is useful to use here the electron hole equivalence for details consult:
| The electron-hole equivalence
|
|
In the present case, this equivalence can be used to transform a problem of 4-orbital determinants into a simpler problem of 2-orbital determinants.
This goes as follows. Whether we reason in the MO framework or in the VB framework, the basis set of orbitals is made of 3 spin-up spinorbitals and 3 spin-down ones. So for each 4-e determinant involving 4 occupied spin-orbitals, we can define a 2-hole determinant involving 2 spin-orbitals, filled with « holes ». Holes have spins and can be represented by up or down arrows just like electrons. There is a one-to-one correspondence between the electron-determinants and the hole-determinants, as shown below :
| electron-filled determinants |
|
hole-filled determinants
|
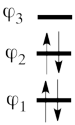 |
|
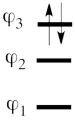
|
| <math> \vert \varphi_1\bar{\varphi_1}\varphi_2\bar{\varphi_2}\vert </math> |
<=> |
<math>\vert \varphi_3\bar{\varphi_3}\vert </math>
|
| Expand into |
|
Expand into
|
| <math> \Phi_{\textrm{1}}= \frac{1}{\sqrt2}(\vert p_1\overline p_1p_2\overline p_3\vert + \vert p_1\overline p_1p_3\overline p_2\vert </math> |
<=> |
<math> \frac{1}{\sqrt2}(\vert p_2\overline p_3 \vert + \vert p_3\overline p_2\vert </math>
|
| <math> \Phi_{\textrm{2}}= \frac{1}{\sqrt2}(\vert p_3\overline p_3p_1\overline p_2\vert + \vert p_3\overline p_3p_2\overline p_1\vert </math> |
<=> |
<math> \frac{1}{\sqrt2}(\vert p_1\overline p_2 \vert + \vert p_2\overline p_1\vert </math>
|
| <math> \Phi_{\textrm{3}}= \frac{1}{\sqrt2}(\vert p_2\overline p_2p_1\overline p_3\vert + \vert p_2\overline p_2p_3\overline p_1\vert </math> |
<=> |
<math> \frac{1}{\sqrt2}(\vert p_1\overline p_3 \vert + \vert p_3\overline p_1\vert </math>
|
| <math> \Phi_{\textrm{4}}= \vert p_1\overline p_1p_3\overline p_3\vert </math> |
<=> |
<math> \vert p_2\overline p_2 \vert </math>
|
| <math> \Phi_{\textrm{5}}= \vert p_1\overline p_1p_2\overline p_2\vert </math> |
<=> |
<math> \vert p_3\overline p_3 \vert </math>
|
| <math> \Phi_{\textrm{6}}= \vert p_2\overline p_2p_3\overline p_3\vert </math> |
<=> |
<math> \vert p_1\overline p_1 \vert </math>
|
So instead of expanding the Hartree-Fock electron determinant <math> \vert \varphi_1\bar{\varphi_1}\varphi_2\bar{\varphi_2}\vert </math> into VB structures, which is complicated, we better expand the smaller complementary hole-determinant <math>\vert \varphi_3\bar{\varphi_3}\vert </math> into VB structures where each contains two holes. Once this is done, it suffices to use the table above to go back to the 4-electron VB structures (e.g. <math> \vert p_2\overline p_2 \vert </math> => <math> \vert p_1\overline p_1p_3\overline p_3\vert </math> and so on). This latter transformation gives us the final 4-e VB function.
|
|
|
|