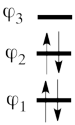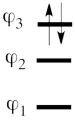Différences entre les versions de « The electron-hole equivalence »
(The electron-hole equivalence) |
|||
| Ligne 40 : | Ligne 40 : | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
So instead of expanding the Hartree-Fock electron determinant <math> \vert \varphi_1\bar{\varphi_1}\varphi_2\bar{\varphi_2}\vert </math> into VB structures, which is complicated, we better expand the smaller complementary hole-determinant <math>\vert \varphi_3\bar{\varphi_3}\vert </math> into VB structures where each contains two holes. Once this is done, it suffices to use the table above to go back to the 4-electron VB structures (e.g. <math> \vert p_2\overline p_2 \vert </math> => <math> \vert p_1\overline p_1p_3\overline p_3\vert </math> and so on). This latter transformation gives us the final 4-e VB function.<br> | So instead of expanding the Hartree-Fock electron determinant <math> \vert \varphi_1\bar{\varphi_1}\varphi_2\bar{\varphi_2}\vert </math> into VB structures, which is complicated, we better expand the smaller complementary hole-determinant <math>\vert \varphi_3\bar{\varphi_3}\vert </math> into VB structures where each contains two holes. Once this is done, it suffices to use the table above to go back to the 4-electron VB structures (e.g. <math> \vert p_2\overline p_2 \vert </math> => <math> \vert p_1\overline p_1p_3\overline p_3\vert </math> and so on). This latter transformation gives us the final 4-e VB function.<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[VBTutorial2|<< Return to the Tutorial-2]] | ||
Dernière version du 8 juillet 2012 à 22:45
The electron-hole equivalence
In the present case, this equivalence can be used to transform a problem of 4-orbital determinants into a simpler problem of 2-orbital determinants.
This goes as follows. Whether we reason in the MO framework or in the VB framework, the basis set of orbitals is made of 3 spin-up spinorbitals and 3 spin-down ones. So for each 4-e determinant involving 4 occupied spin-orbitals, we can define a 2-hole determinant involving 2 spin-orbitals, filled with « holes ». Holes have spins and can be represented by up or down arrows just like electrons. There is a one-to-one correspondence between the electron-determinants and the hole-determinants, as shown below :
So instead of expanding the Hartree-Fock electron determinant <math> \vert \varphi_1\bar{\varphi_1}\varphi_2\bar{\varphi_2}\vert </math> into VB structures, which is complicated, we better expand the smaller complementary hole-determinant <math>\vert \varphi_3\bar{\varphi_3}\vert </math> into VB structures where each contains two holes. Once this is done, it suffices to use the table above to go back to the 4-electron VB structures (e.g. <math> \vert p_2\overline p_2 \vert </math> => <math> \vert p_1\overline p_1p_3\overline p_3\vert </math> and so on). This latter transformation gives us the final 4-e VB function.